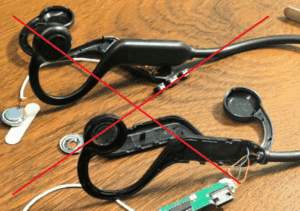
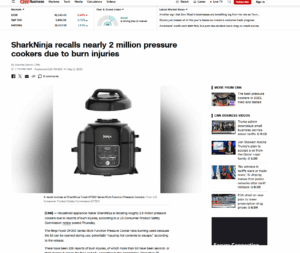
The Three Core Functions of Quality Inspection
Quality control (QC) plays a vital role in manufacturing, ensuring product reliability, reducing defects, and maintaining brand reputation. The three primary functions of QC are:
1. Assurance Function
The foundation of quality inspection is to ensure that only materials, components, and finished products that meet quality standards proceed to the next stage. By inspecting raw materials, semi-finished goods, and final products, defective items are identified and eliminated, preventing costly rework, recalls, and customer dissatisfaction.
2. Preventive Function
Quality inspection is not just about rejecting faulty products—it’s about preventing defects before they occur. By detecting issues early, root causes can be identified and resolved, reducing the risk of defective batches. A proactive quality team minimizes production waste, optimizes costs, and enhances overall efficiency.
3. Reporting Function
Comprehensive documentation and analysis of QC data provide insights into production trends, potential risks, and areas for improvement. Regular reports enable informed decision-making, continuous process refinement, and higher-quality product outcomes.
Four Steps for Handling Quality Issues
Despite stringent controls, occasional quality issues arise. When this happens, an effective four-step process ensures swift resolution:
1. Identification
All suspected defective batches are clearly marked, separating them from conforming products to prevent accidental use.
2. Isolation
Faulty products are moved to designated areas to avoid cross-contamination and ensure they do not proceed further in production.
3. Reporting
Inspection teams document defects and report them to management for review and corrective action determination.
4. Follow-Up
Corrective actions are implemented, and re-inspections confirm defect resolution, preventing recurrence and reinforcing process improvements.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): First Line of Defense
Purpose & Importance
IQC is the initial checkpoint to verify the quality of incoming raw materials, components, and outsourced parts before they enter production. A robust IQC process prevents defective materials from compromising the final product.
Responsibilities of IQC Teams
Inspect raw materials and components according to acceptance criteria.
Label materials based on inspection results (approved, rejected, or conditional acceptance).
Document and report issues, escalating them for review if necessary.
Work with suppliers to resolve recurring quality concerns.
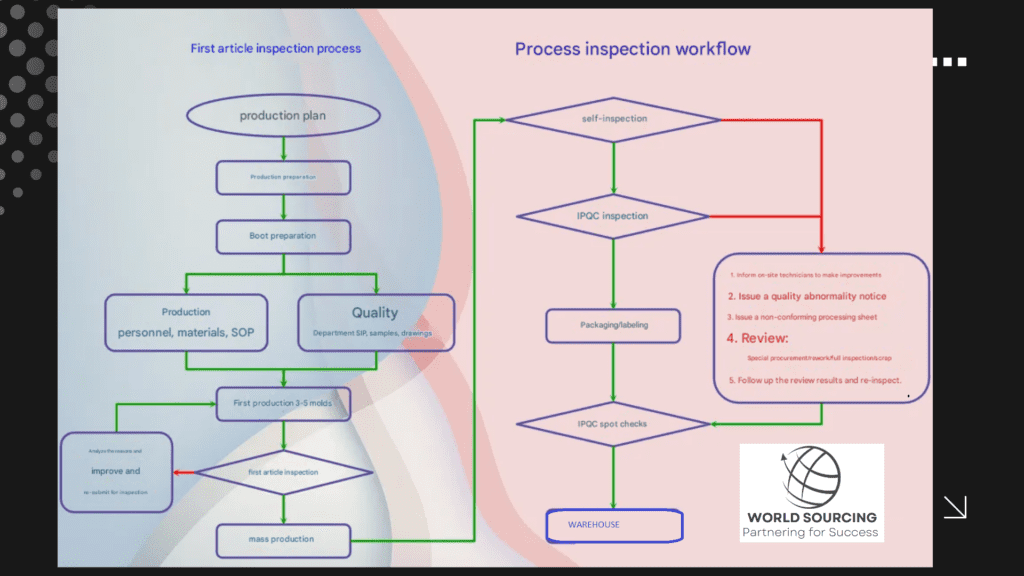
Standard IQC Workflow
Supplier Delivery – Raw materials arrive at the warehouse.
Temporary Storage – Items are held in a designated quarantine area.
Inspection – QC personnel conduct sampling and full inspections.
Approval for Use – Accepted materials are moved to production, while defective ones are flagged for corrective action.
Corrective Measures – Suppliers receive reports and are required to implement corrective actions.
Outgoing Quality Control (OQC): Final Product Validation
Purpose
OQC ensures that finished products meet client specifications before shipment. A well-executed OQC process reduces the risk of product returns, customer complaints, and reputational damage.
Responsibilities of OQC Teams
Conduct final inspections on finished products.
Document findings and complete inspection reports.
Label products according to their inspection status.
Report any deviations and coordinate corrective actions.
Standard OQC Workflow
Shipment Order Received – The warehouse prepares products for shipment.
Pre-Shipment Inspection – QC teams verify compliance with specifications.
Approval & Labeling – Approved batches are cleared for shipping.
Defective Product Management – Any issues trigger further investigation and resolution.
Customer Communication – Clients are informed of any relevant findings, ensuring transparency.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ensuring Consistency in Production
Purpose
IPQC involves real-time inspections during manufacturing, allowing early detection of defects and preventing mass production of faulty goods. This continuous monitoring enhances efficiency and reduces waste.
Responsibilities of IPQC Teams
Verify product specifications during each production phase.
Conduct first-piece inspections before mass production begins.
Perform routine checks at specified intervals.
Identify and address process deviations immediately.
Ensure compliance with Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs).
Standard IPQC Workflow
First-Piece Inspection – The first manufactured unit is examined to confirm setup accuracy.
Routine Inspections – QC personnel conduct periodic checks.
Defect Isolation – Any non-conforming items are flagged and isolated.
Corrective Actions – Root causes are analyzed, and production is adjusted accordingly.
Final Verification – Ensuring that all corrective actions have been effective before continuing production.
Partner with Us for Unmatched OEM Quality Excellence
At World Sourcing Ltd., we don’t just manufacture products—we craft high-quality, innovative solutions tailored to your brand’s success. Our rigorous quality control processes ensure that every component and finished product meets the highest industry standards, reducing risks and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Whether you’re looking for a trusted OEM partner for heated mugs, smart technology, or customized consumer goods, our expert team is ready to deliver superior quality and seamless production.
🔹 Ready to boost your product quality and streamline your supply chain? 📩 Contact us today and discover the future of reliable, high-performance manufacturing!





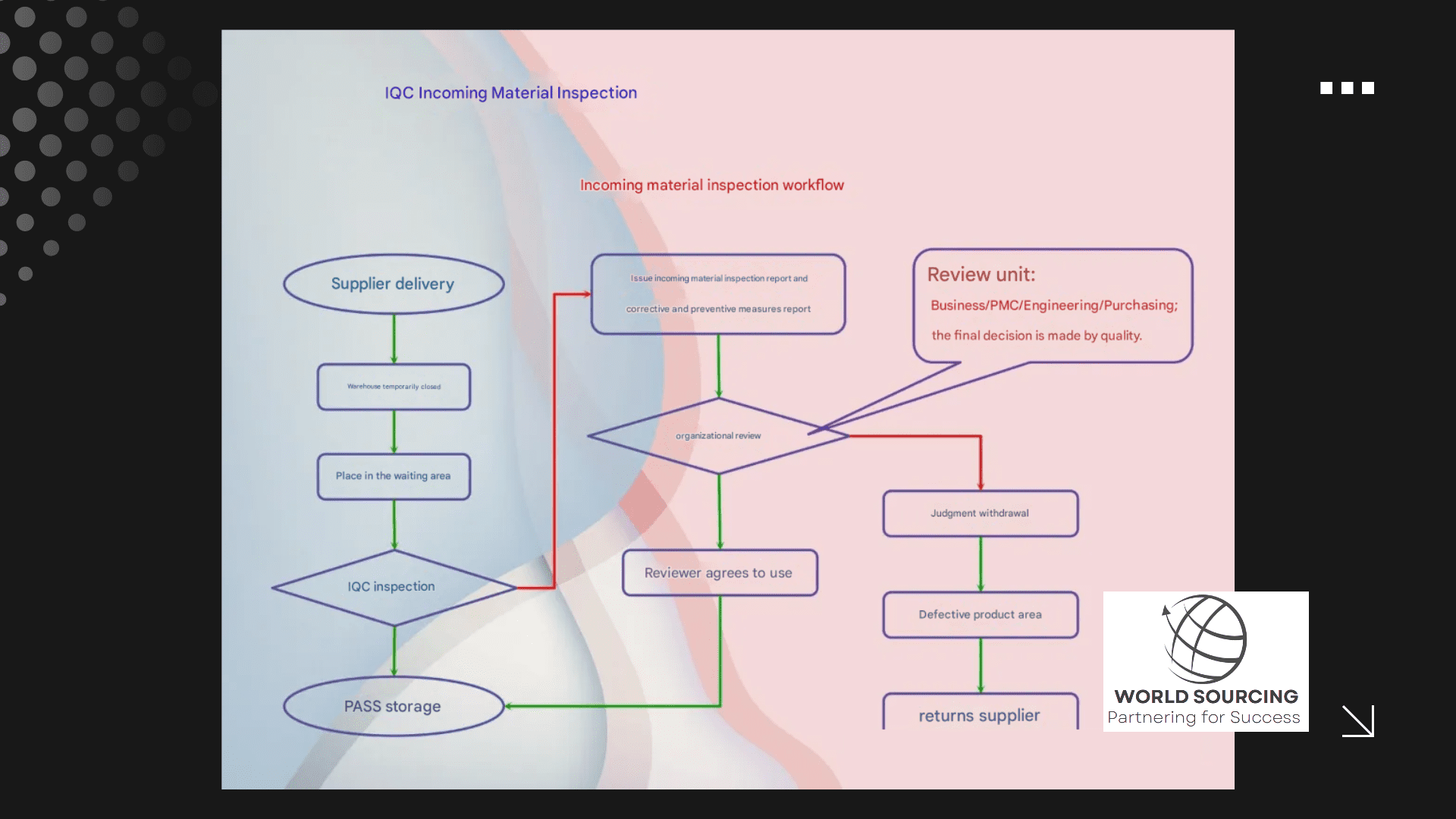

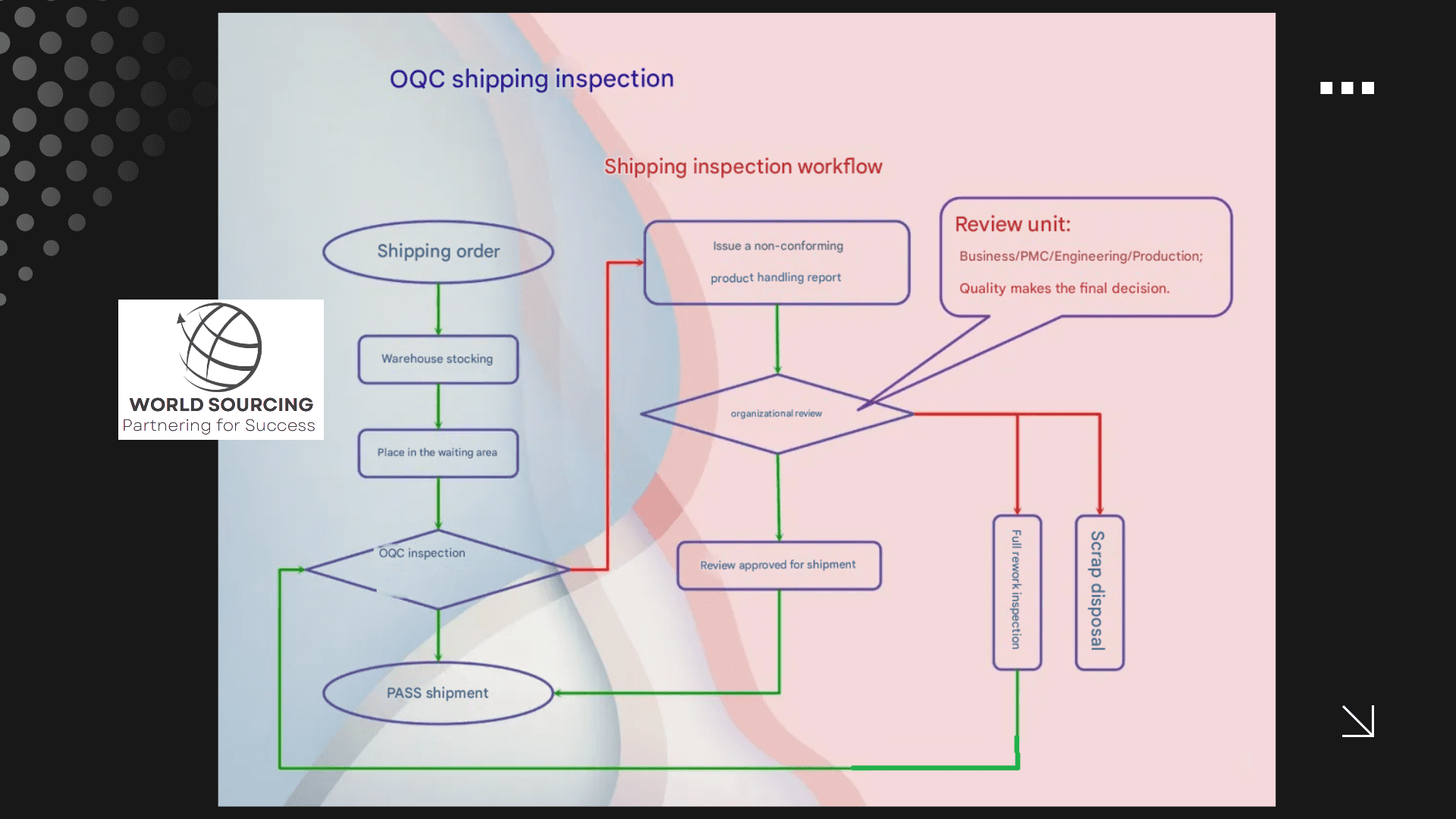



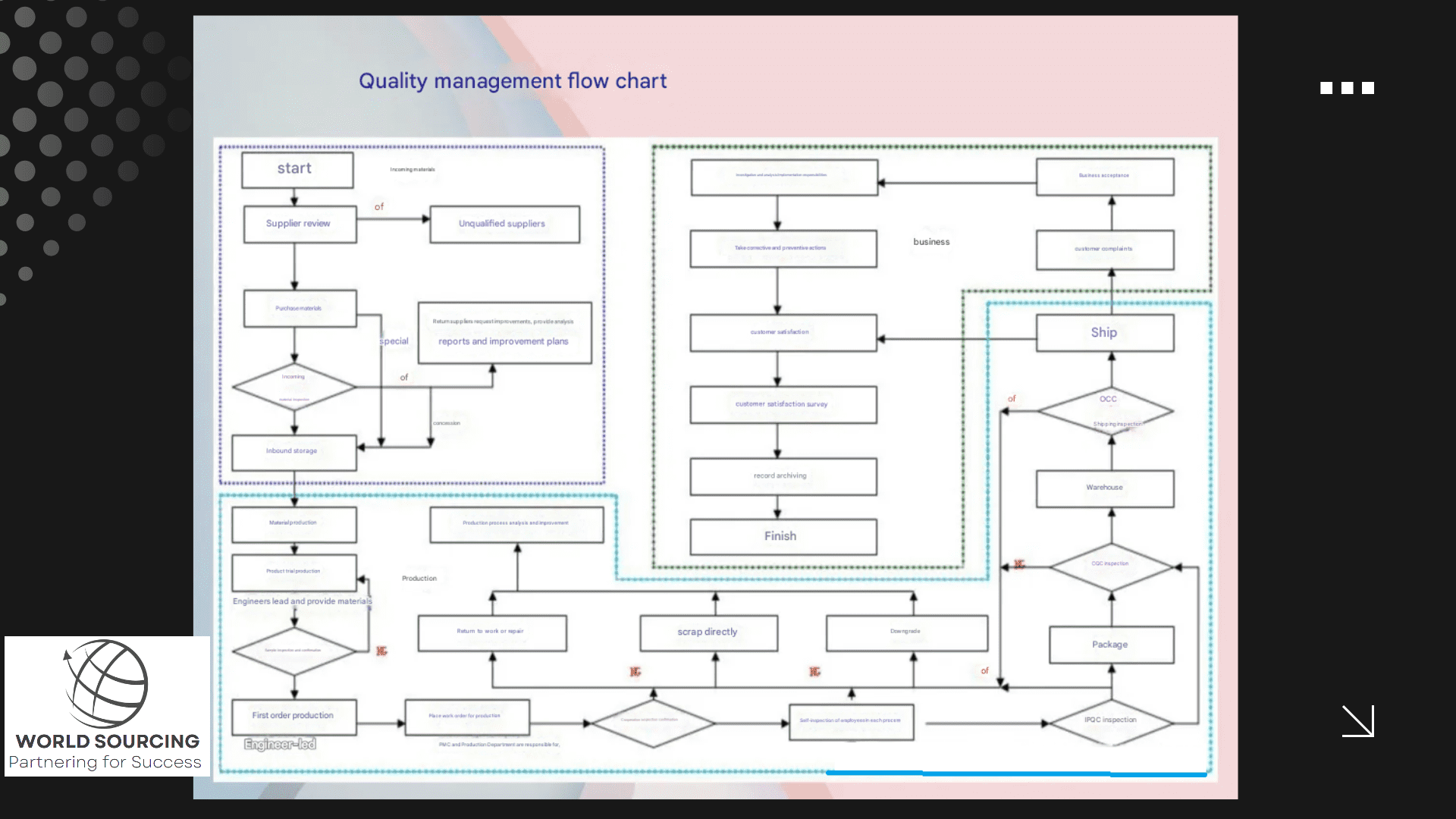

Internal QC , method, flow, diagram desgined by Joe Liang, QC Manager, World Sourcing Ltd.